A Beginner’s Guide: Multi-State Payroll Compliance Legislation
- Aesha Shah
- September 26, 2025
- 6 minutes
Managing payroll across multiple states requires more than just cutting paychecks. It means accurately calculating salaries, withholding the correct taxes, and ensuring timely payments for employees working in different jurisdictions.
The complexity arises because each state enforces its own regulations, tax laws, and reporting obligations, making compliance a demanding task for businesses.
Even a small error, such as miscalculating tax withholdings or overlooking a reporting deadline, can place your business at risk of audits, penalties, and reputational damage. That’s why understanding multi-state payroll compliance legislation is not just a legal necessity but a strategic safeguard.
For businesses also navigating global operations, leveraging accounting outsourcing and other offshore outsourcing services can provide scalable back-office efficiency and compliance support.
This guide serves as a practical starting point to help employers remain compliant, streamline processes, and protect their organization from costly pitfalls.
Key Takeaway
- Multi-state payroll involves complex salary calculations, tax withholdings, and timely payments, with mistakes risking audits, penalties, and reputational damage.
- Key elements include state and local tax withholding, unemployment insurance, labor law compliance, and accurate reporting, often supported by a payroll compliance practitioner online or outsourced bookkeeping services.
- Best practices include using an advanced payroll management system, partnering with payroll experts, maintaining clear internal processes, and staying updated on state-specific requirements.
- Strategic compliance reduces risks, enhances operational efficiency, and supports growth through solutions like outsourced SMSF compliance and outsourced payables.
What is Multi-State Payroll?
Multi-state payroll refers to the process of managing wages, tax withholdings, and compliance requirements for employees who work across different state jurisdictions.
For businesses with remote teams, traveling staff, or operations spread across multiple states, this becomes a critical responsibility.
At its core, multi-state payroll compliance legislation ensures that employers meet the unique tax laws, labor regulations, and reporting obligations of each state where their employees are active.
Understanding these requirements is essential not only for avoiding penalties but also for building a payroll system that supports growth and flexibility.
Key elements involved in multi-state payroll include payroll outsourcing and implementing robust outsourced payroll services to maintain compliance while reducing manual errors.
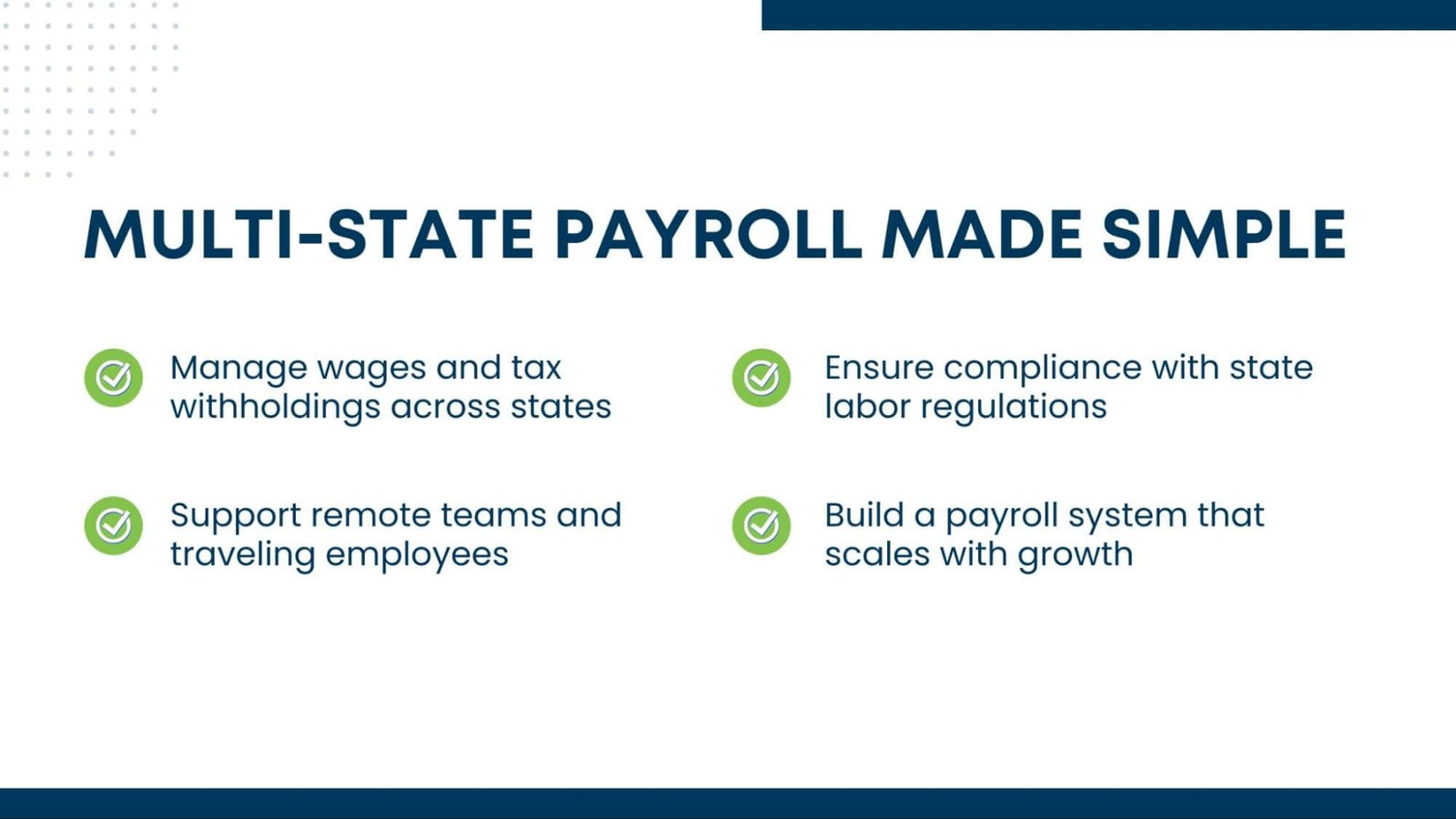
Key elements involved in multi-state payroll include:
State and Local Income Tax Withholding
For multi-state employers, calculating the correct income tax for each employee involves navigating a complex mix of state and local regulations. Here are the key considerations under multi-state payroll compliance legislation:
- Work Location vs. Residency: Generally, income tax should be withheld based on the state where the employee performs their job duties. Residency rules may also apply, particularly if employees live in one state and work in another.
- Remote and Traveling Employees: For employees who work remotely or travel frequently, employers must determine if they have created a taxable “nexus” with the state. A nexus establishes whether the business is required to withhold state income taxes.
- De Minimis Rules: Some states allow limited work within their borders before triggering tax withholding obligations, while others require withholding for any work performed, regardless of duration.
- Reciprocal Agreements: Certain states have reciprocal tax agreements, meaning employees are taxed only in their state of residence, even if they work elsewhere.
- Local Taxes: In addition to state income tax, employers may also need to account for city, county, or other local tax requirements, which can add another layer of complexity.
Unemployment Insurance Taxes
Under multi-state payroll compliance legislation, employers must carefully manage unemployment insurance (UI) taxes, which are determined by the state where employees perform their work duties, not where they reside.
For fully remote teams, the state in which the employer’s headquarters is located generally governs unemployment insurance obligations.
Key points to understand include:
- Federal-State Program: Unemployment insurance is a joint initiative designed to provide temporary financial support to workers who lose their jobs through no fault of their own.
- SUTA (State Unemployment Tax Act): This program is partially funded by the federal government but administered at the state level. Each state sets its own unemployment tax requirements.
- Variable Tax Rates: States determine their unique unemployment insurance tax rate, wage base limits, and compliance guidelines, which can change over time.
- Employer Responsibility: Businesses must register with the appropriate state agency and remit unemployment insurance contributions accurately to avoid penalties and remain compliant.
Outsourcing elements of compliance, such as financial compliance or regulatory compliance, can further ease this burden.
Compliance with State Labor Laws
Managing multi-state payroll also requires adherence to each state’s unique labor regulations. Employers must consider:
- Minimum Wage Requirements: Ensuring employee pay meets or exceeds state-specific minimum wage laws.
- Overtime Rules: Calculating and compensating overtime in compliance with the regulations of each state.
- Leave Policies: Observing state-mandated paid leave, sick leave, and family leave provisions.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Maintaining coverage that meets state-specific requirements.
- Other Employment Regulations: Staying compliant with additional state labor laws, such as employee classification and workplace safety standards.
Reporting and Filing
Accurate and timely reporting is essential under multi-state payroll compliance legislation. Many businesses now rely on a payroll compliance practitioner online to stay updated with changing tax laws, file returns correctly, and ensure documentation is submitted on time to the appropriate state agencies.
This online support can be especially valuable for companies managing employees across multiple jurisdictions.
Key responsibilities include:
- Payroll Tax Filings: Submitting state and local tax returns, wage reports, and other required documentation.
- Staying Informed: Monitoring changes in state labor and tax laws to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Deadlines and Accuracy: Meeting all reporting deadlines and maintaining accurate records to avoid penalties and legal issues.
Organizations that already work with outsourced bookkeeping services or professional bookkeeping services often integrate reporting into their broader compliance systems.
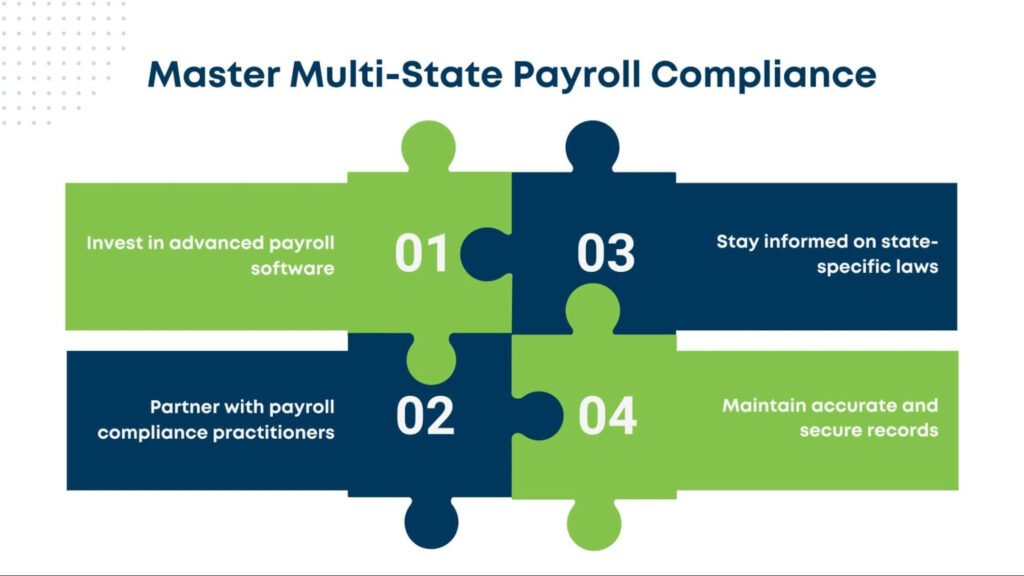
Best Practices to Navigate Multi-State Payroll
Managing payroll across multiple states introduces significant complexity for HR and accounting teams. Differing state regulations, tax rates, and wage-and-hour laws demand meticulous planning and execution to ensure compliance.
With the right processes and tools, businesses can reduce risks while maintaining accurate, timely employee compensation. Here are some best practices for efficient multi-state payroll compliance legislation:
- Invest in an Advanced Payroll Management System: Automating federal, state, and local tax requirements reduces manual errors and ensures accurate tax calculations and timely filings. Consider integrating with virtual CFO services for deeper insights.
- Partner with Payroll Processing Services or Tax Experts: Engaging a professional payroll compliance practitioner or tax advisor can help your business stay updated on evolving regulations across jurisdictions. Expert guidance supports accurate compliance, minimizes penalties, and simplifies complex scenarios.
- Establish Clear Internal Processes: Implement robust procedures to collect, validate, and maintain employee data, including work locations, states of residence, and pay rates. Conduct regular internal audits to identify and correct discrepancies in payroll processing and tax filings.
- Stay Informed About State-Specific Requirements: Monitor updates to tax rates, wage base limits, and reporting deadlines for every state where your employees operate. Awareness of changes ensures timely compliance.
- Maintain Accurate and Secure Records: Keep detailed payroll records, including pay stubs, tax filings, and supporting documentation. Implement strong security measures to safeguard sensitive employee data from unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Navigating multi-state payroll compliance legislation may seem complex, but with a structured approach, the right tools, and expert guidance, businesses can effectively manage payroll across multiple jurisdictions.
Investing in an advanced employee payroll management system or human resource payroll system, partnering with experienced practitioners, and leveraging solutions like outsourced SMSF compliance or outsourced payables creates stronger compliance frameworks.
By staying informed, implementing robust processes, and leveraging technology, employers can minimize risks, avoid penalties, and focus on what matters most: supporting their workforce and driving business growth.
Compliance is not just a legal obligation; it’s a strategic advantage that strengthens your credibility, supports your workforce, and drives operational efficiency. To learn more about optimizing payroll and compliance, contact our team today.